Building as Pedagogy: Oberlin's Adam Joseph Lewis Center

RESEARCH LEGACY: personal reflections on a career in research
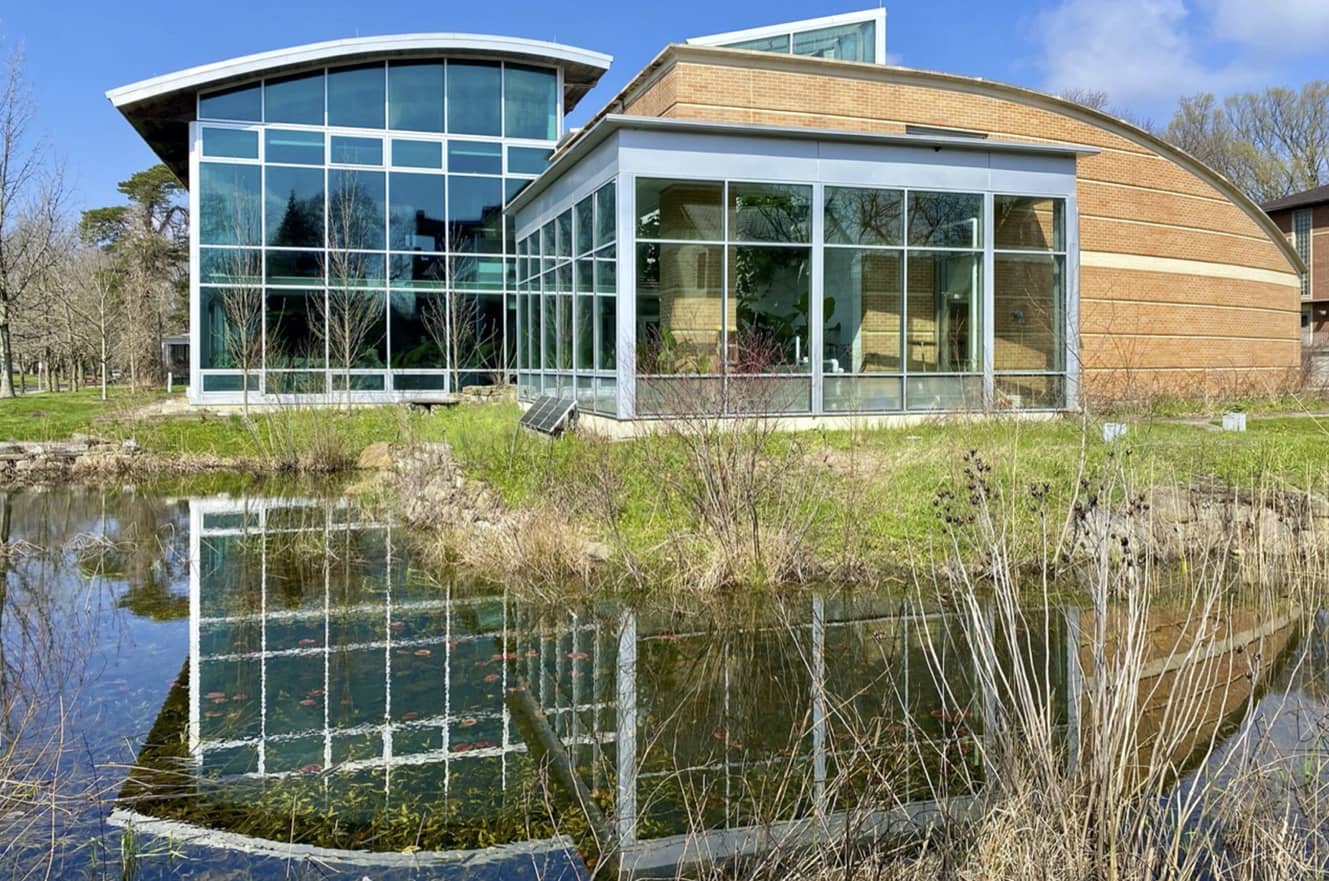
David Orr (Oberlin College) explains how a radical building project to 'design with nature' had profound impacts on education as well as inspiring students, designers and the wider community. The Adam Joseph Lewis Center is a milestone building. With ingenuity and effort, it provided a positive message that we can design neighborhoods, communities, cities, and nations to enhance the biosphere. It continues to provide many lessons for designers and students.
Context
When I arrived at Oberlin College in August of 1990, the Environmental Studies Program was located in two rooms in the basement of a solid three-story stone hulk, built in 1910. I was the single faculty member in a fledgling program with seven majors in a liberal arts college and conservatory. Environmental Studies was designated a program, not a department, the difference being the breadth of the subject across many disciplines. Most issues within its purview, such as climate change, sprawled across multiple disciplines. Climate change, however, is the sum total of many factors and did not fit easily into a structure organized like a series of pidgeon-holes (or silos) as separate disciplines. This reflects a larger problem in the organization of knowledge in which analysis by the method of reducing things to their component parts (“reductionism”), is regarded as the quintessence of rigor while much less emphasis is placed on synthesis and systems analysis. Big issues often fall through the cracks including the relation between learning and the design of educational facilities.
As interest in environmental studies grew, it became clear that the program needed a larger space for offices and classes. In response, we conducted a yearlong course in 1992-93 with leading architects on the emerging field of ecological design appropriate to re-modelling an existing building or building something new. Throughout the year, students wrote articles on the class for the newspaper helping to build a solid constituency for the project and interest in ’green‘ architecture. Two years later the College Trustees approved the project but assumed that it would fail for lack of funding. They maintained a prudent distance from the project that allowed us to expand the scope of the project without interference.
Beginning in the summer of 1995, we proceeded along two lines: one to raise the funding, the other entailed organizing thirteen design charrettes open to all students and to the wider community to build a knowledgeable constituency for the project and to calibrate the design to the larger purposes of the Environmental Studies Program. The project evolved into an experiment in applied hope and ecological design that included on-site water purification, solar technology, use of non-toxic materials, gardens, land restoration, and accurate feedback on building performance. By making various aspects of sustainability visible, practical, and affordable, we aimed to confirm Kenneth Boulding’s suspicion that 'whatever is, is possible.'
The project, in short, was an early attempt to ’design with nature,’ regarding the building and landscape as one system, not a loose federation of isolated components. Further, we aimed “to cause no ugliness human or ecological somewhere else or at some later time.” Such aspirations are beyond mortal attainment, but the striving is no less important for being beyond our grasp, if for no other reason than the damage construction does to the Earth from the extraction, processing, transportation, and disposal of materials. That said, we wrestled with the question of how to balance the ledger in the longer term by generating as much energy as possible on site and using the building as a site for redeeming educational and research activities. The building was intended to be not just a place where classes were held, but a place that educated by its design, operation, and evolution. Architecture, in other words, should be thought a kind of crystalized pedagogy that instructs one way or another (Orr,1994). Building and landscape design can reveal the larger ecological context in which it exists, can inspire hope, build practical competence, and help generate momentum toward a better and more coherent world. Or not.
Outcomes
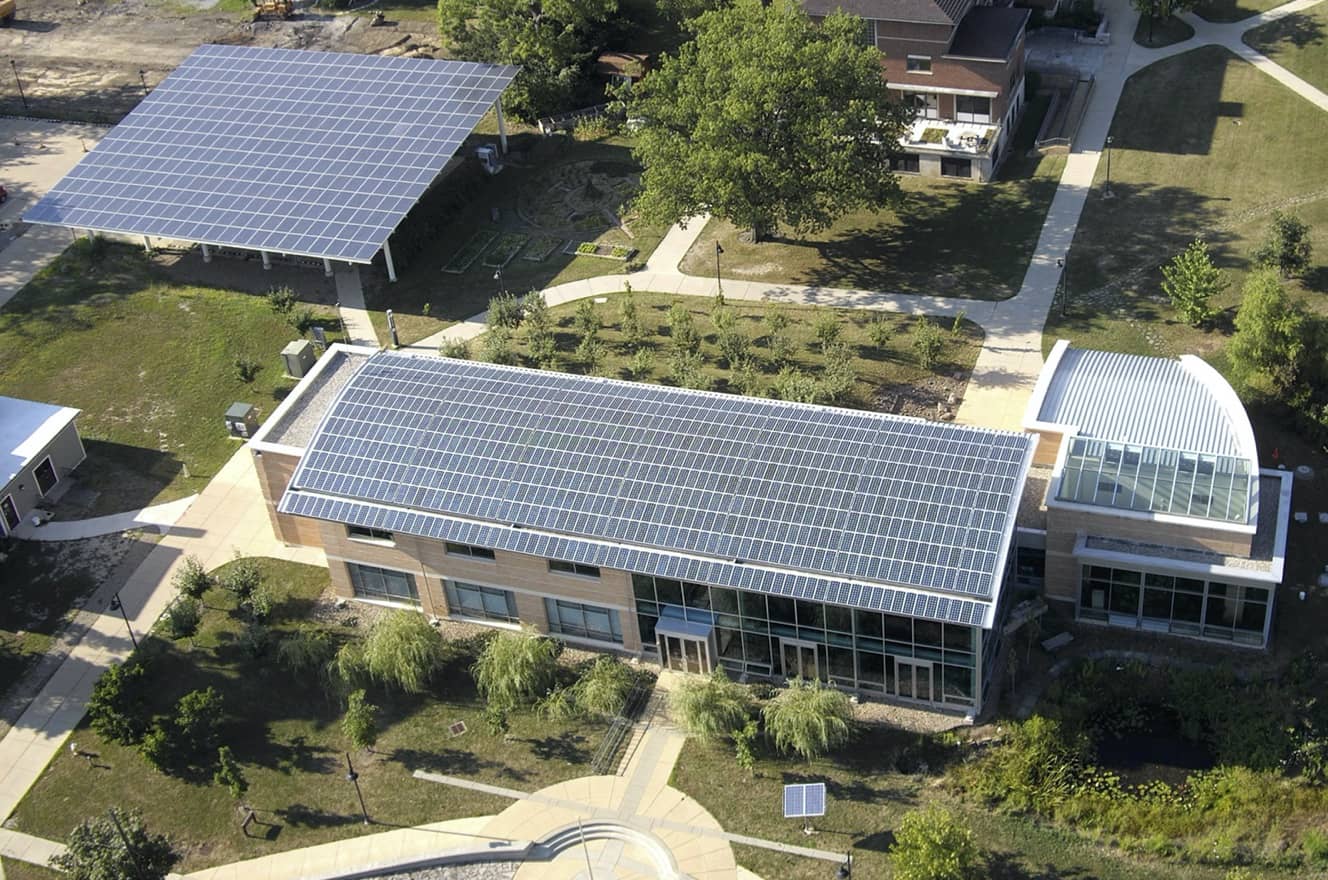

Second, it was an example of integrated design—applied systems thinking—that began in the programing phase and extended through commissioning (Orr, 2006). Third, it was notable as a statement about the value, even the right, of students and community members to participate in the design of the built environment and it offered a practical example of how to solve multiple problems by integrating design. Fourth, it was personal: health was the connecting thread throughout. Human health and healthy environments stood out as a positive response to the tsunami of bad news about the human prospect. Finally, at a small scale the AJLC pointed to larger possibilities. With ingenuity and effort, it provided a clear message that we can design neighborhoods, communities, cities, and nations to fit a planet with a biosphere.
Some reflections
I worry less about the solvability of environmental problems than I do about the despair that young people often feel given the massive scale of the crisis. Buildings like the Lewis Center counter that despair by reducing problems and solutions to a comprehensible scale and building competence in solving problems. In so doing they make reasons for hope visible, the courage to risk plausible, and inspire careers otherwise unimaginable.
For colleges and universities, high performance buildings require learning to manage facilities as systems evolving over time. This requires understanding that the real cost of any facility is not simply the initial costs of design and construction, but the costs for energy, water, and upkeep over its lifetime. Further, the net cost of any building should include long-term benefits to reputation, admissions, educational value, and its role as a catalyst for other things. The AJLC, for example, helped to launch the Oberlin Project, a highly successful eight-year effort to take ecological design to scale in the City of Oberlin; establish climate-neutral policy for both the City and College, introduce issues of sustainability into the curriculum of local schools, increase the market for local agriculture, and stimulate downtown economic renewal (Orr, 2015).
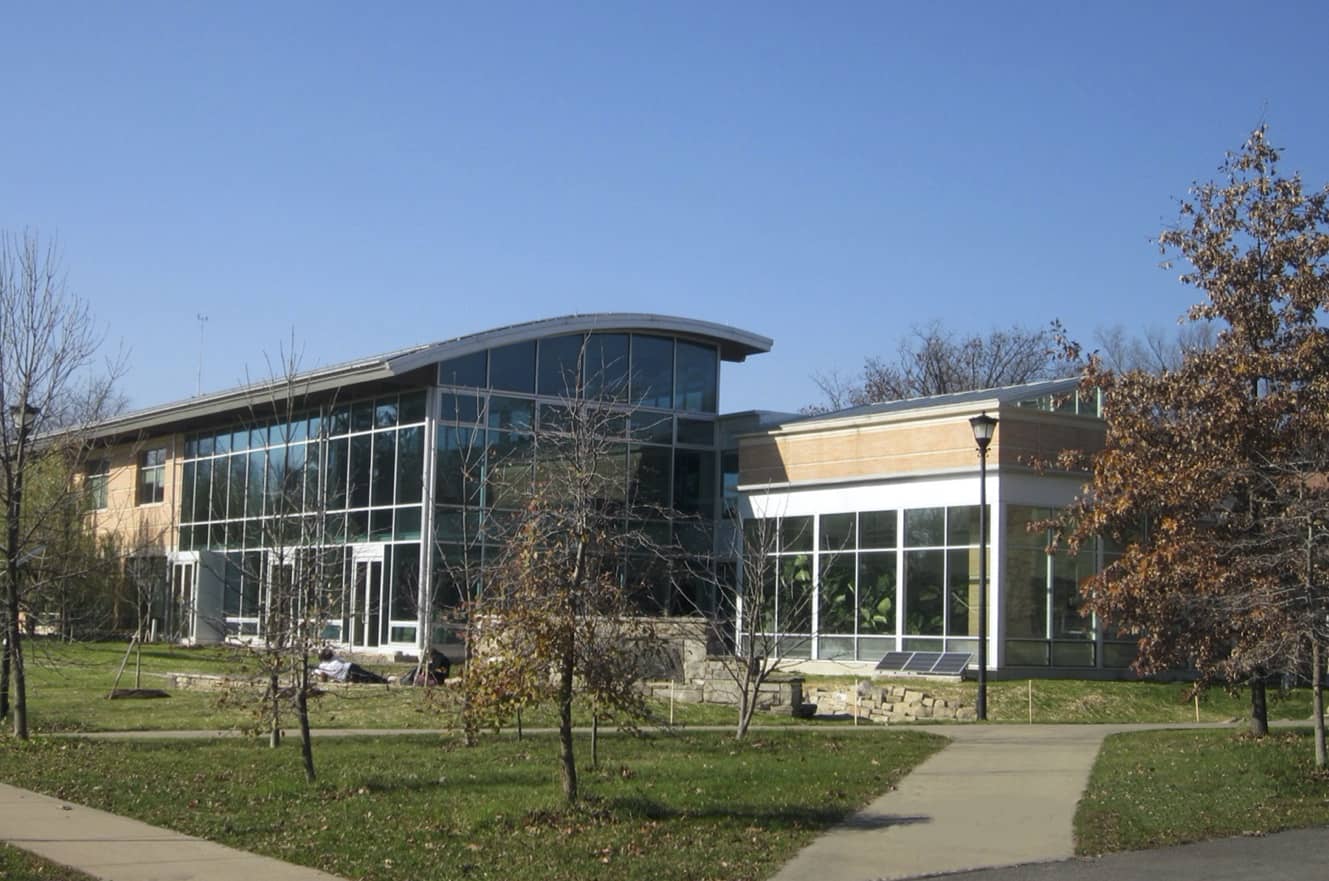

The ecological design of buildings, landscapes, and entire institutions is a subset of a much larger and necessary conversation about how societies make the human presence durable and decent without combustion. That conversation begins by acknowledging the first rule of design disciplined by place is that you do not ruin other places. In this, architecture is particularly important because the built environment—what we see and experience daily—is a powerful determinant of our behavior and our awareness of possibilities. The caveat is that while better design can improve our prospects, we cannot build our way out of our current predicament. At best, superior design can buy us time to understand our situation more clearly, clarify our goals, and create a more beautiful, compassionate, and coherent world than that in prospect.
The great advantage of seeing problems as design not moral failures is that many become solvable or even avoidable with better design. That possibility should launch a larger conversation to clarify and improve our economy, culture, and governance (Orr, 2018). For example: if the writers of the US Constitution in 1787 had known what is now known about how Earth works as a physical system, how would they have designed a Constitution for a world of leads and lags, stocks and flows, time lapses between cause and effects, and positive and negative feedback loops? In that knowledge, how should we reform our government? laws? economy? cities? military as systems interacting with other systems over time?
Finally, on a personal note, it was a privilege to work with a brilliant and dedicated team of colleagues, architects, and designers to meet and overcome the various challenges of making of the AJLC. The mutual respect, camaraderie and sense of achievement we shared was worth all the risk, hassle, criticism, worry, and late nights in airports far from home. The challenge to step out of the abstract academic world into that of architecture, engineering, landscape design, materials, budgets i.e. tangible realities changed and enriched my perspective in more ways than I can count. It was a gift in every way and I am grateful for it.
To students, I suggest that you take the path less traveled; aim to be a ’radical professional‘ the kind of person who takes risks, raises the stakes, connects otherwise disparate things, sees the farther horizon. At whatever scale you choose to work do it as if the future of civilization depends on it because in some measure it does (Schmidt, 2000, 265-280). To educators and designers the most important challenge you face is that of creating “a more consequential, professional discipline” appropriate to the challenges of designing a more just, durable, coherent, and beautiful civilization (Walker, 2014, 39).
References
Orr, David W. (1994). Architecture as Pedagogy, in Orr, Earth in Mind. (Second edition, 2004) Washington, D.C.: Island Press.
Orr, David W. (2006). Design on the Edge: The Making of a High Performance Building. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Orr, David W. (2015). The Oberlin Project. Solutions.
Orr, David W. (2018). The Political Economy of Design in a Hotter Time, in Rachel Beth Egenhoefer (ed), Routledge Handbook of Sustainable Design. London: Routledge.
Schmidt, Jeff (2000). Disciplined Minds. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
Walker, Stuart (2014). Designing Sustainability. London: Routledge.
Share:
Latest Peer-Reviewed Journal Content
Spatiotemporal evaluation of embodied carbon in urban residential development
I Talvitie, A Amiri & S Junnila
Energy sufficiency in buildings and cities: current research, future directions [editorial]
M Sahakian, T Fawcett & S Darby
Sufficiency, consumption patterns and limits: a survey of French households
J Bouillet & C Grandclément
Health inequalities and indoor environments: research challenges and priorities [editorial]
M Ucci & A Mavrogianni
Operationalising energy sufficiency for low-carbon built environments in urbanising India
A B Lall & G Sethi
Promoting practices of sufficiency: reprogramming resource-intensive material arrangements
T H Christensen, L K Aagaard, A K Juvik, C Samson & K Gram-Hanssen
Culture change in the UK construction industry: an anthropological perspective
I Tellam
Are people willing to share living space? Household preferences in Finland
E Ruokamo, E Kylkilahti, M Lettenmeier & A Toppinen
Towards urban LCA: examining densification alternatives for a residential neighbourhood
M Moisio, E Salmio, T Kaasalainen, S Huuhka, A Räsänen, J Lahdensivu, M Leppänen & P Kuula
A population-level framework to estimate unequal exposure to indoor heat and air pollution
R Cole, C H Simpson, L Ferguson, P Symonds, J Taylor, C Heaviside, P Murage, H L Macintyre, S Hajat, A Mavrogianni & M Davies
Finnish glazed balconies: residents’ experience, wellbeing and use
L Jegard, R Castaño-Rosa, S Kilpeläinen & S Pelsmakers
Modelling Nigerian residential dwellings: bottom-up approach and scenario analysis
C C Nwagwu, S Akin & E G Hertwich
Mapping municipal land policies: applications of flexible zoning for densification
V Götze, J-D Gerber & M Jehling
Energy sufficiency and recognition justice: a study of household consumption
A Guilbert
Linking housing, socio-demographic, environmental and mental health data at scale
P Symonds, C H Simpson, G Petrou, L Ferguson, A Mavrogianni & M Davies
Measuring health inequities due to housing characteristics
K Govertsen & M Kane
Provide or prevent? Exploring sufficiency imaginaries within Danish systems of provision
L K Aagaard & T H Christensen
Imagining sufficiency through collective changes as satisfiers
O Moynat & M Sahakian
US urban land-use reform: a strategy for energy sufficiency
Z M Subin, J Lombardi, R Muralidharan, J Korn, J Malik, T Pullen, M Wei & T Hong
Mapping supply chains for energy retrofit
F Wade & Y Han
Operationalising building-related energy sufficiency measures in SMEs
I Fouiteh, J D Cabrera Santelices, A Susini & M K Patel
Promoting neighbourhood sharing: infrastructures of convenience and community
A Huber, H Heinrichs & M Jaeger-Erben
New insights into thermal comfort sufficiency in dwellings
G van Moeseke, D de Grave, A Anciaux, J Sobczak & G Wallenborn
‘Rightsize’: a housing design game for spatial and energy sufficiency
P Graham, P Nourian, E Warwick & M Gath-Morad
Implementing housing policies for a sufficient lifestyle
M Bagheri, L Roth, L Siebke, C Rohde & H-J Linke
The jobs of climate adaptation
T Denham, L Rickards & O Ajulo
Structural barriers to sufficiency: the contribution of research on elites
M Koch, K Emilsson, J Lee & H Johansson
Life-cycle GHG emissions of standard houses in Thailand
B Viriyaroj, M Kuittinen & S H Gheewala
IAQ and environmental health literacy: lived experiences of vulnerable people
C Smith, A Drinkwater, M Modlich, D van der Horst & R Doherty
Living smaller: acceptance, effects and structural factors in the EU
M Lehner, J L Richter, H Kreinin, P Mamut, E Vadovics, J Henman, O Mont & D Fuchs
Disrupting the imaginaries of urban action to deliver just adaptation [editorial]
V Castán-Broto, M Olazabal & G Ziervogel
Building energy use in COVID-19 lockdowns: did much change?
F Hollick, D Humphrey, T Oreszczyn, C Elwell & G Huebner
Evaluating past and future building operational emissions: improved method
S Huuhka, M Moisio & M Arnould
Normative future visioning: a critical pedagogy for transformative adaptation
T Comelli, M Pelling, M Hope, J Ensor, M E Filippi, E Y Menteşe & J McCloskey
Nature for resilience reconfigured: global- to-local translation of frames in Africa
K Rochell, H Bulkeley & H Runhaar
How hegemonic discourses of sustainability influence urban climate action
V Castán Broto, L Westman & P Huang
Fabric first: is it still the right approach?
N Eyre, T Fawcett, M Topouzi, G Killip, T Oreszczyn, K Jenkinson & J Rosenow
Social value of the built environment [editorial]
F Samuel & K Watson
Understanding demolition [editorial]
S Huuhka
Data politics in the built environment [editorial]
A Karvonen & T Hargreaves

Latest Commentaries
Systems Thinking is Needed to Achieve Sustainable Cities
As city populations grow, a critical current and future challenge for urban researchers is to provide compelling evidence of the medium and long-term co-benefits of quality, low-carbon affordable housing and compact urban design. Philippa Howden-Chapman (University of Otago) and Ralph Chapman (Victoria University of Wellington) explain why systems-based, transition-oriented research on housing and associated systemic benefits is needed now more than ever.
Unmaking Cities Can Catalyse Sustainable Transformations
Andrew Karvonen (Lund University) explains why innovation has limitations for achieving systemic change. What is also needed is a process of unmaking (i.e. phasing out existing harmful technologies, processes and practices) whilst ensuring inequalities, vulnerabilities and economic hazards are avoided. Researchers have an important role to identify what needs dismantling, identify advantageous and negative impacts and work with stakeholders and local governments.