
www.buildingsandcities.org/insights/news/energy-policy-urban-ghg.html
Impacts of Energy Policy on Urban GHG Emissions

Which combination of policy measures are most appropriate for reducing urban emissions? New peer-reviewed research shows how economic, technology and urban building energy models can be combined and used to evaluate policy efficacy.
Until now, uncertainties of
economic and market-driven factors in urban building energy models (UBEM) have
been a challenge for building energy modellers. The spatial impact of energy
and emissions policies in urban environments is often hard to determine. UBEMs
often fail to recognise the financial and social influences over new buildings
and/ or retrofitting existing building stocks. In INTEGRATION OF AN ENERGY-ECONOMY MODEL WITH AN URBAN ENERGY MODEL, Lu et al. present a new
approach for integrating these different types of model. Specifically, the
authors integrate outputs from a spatial economic model with a spatially
explicit community-level UBEM. This is a major contribution in the development
of an integrated modelling approach, but also in quantifying the co-benefits of
multi-scale effects of energy and emission reduction policies.
Lu et al. adopt a 'sandbox' approach to simulate urban form and building retrofit policies, working at a neighbourhood scale. The sandbox represents a particular urban form, including population density, street pattern, block size and land-use proportions, all derived from a real neighbourhood. This allows for an increasingly realistic representation of the integrated processes that influence energy-usage and emissions output, including fuel choice, building design, mechanical systems, urban form and behaviour.
With this combination, the researchers have been able to model the evolution of a neighbourhood's individual buildings (HVAC system and the building shell) over time. This provides a much higher level of granularity than many existing efforts to understand how building stock changes over time in response to different policy strategies. The interaction between building technology policies and different urban growth-management strategies can be better understood and harnessed. Policy makers are afforded extremely valuable and detailed insights into the impact of energy policies at an individual building-level, prior to their implementation. Insights arising from this combined model will assist practitioners involved in both city planning and energy management.
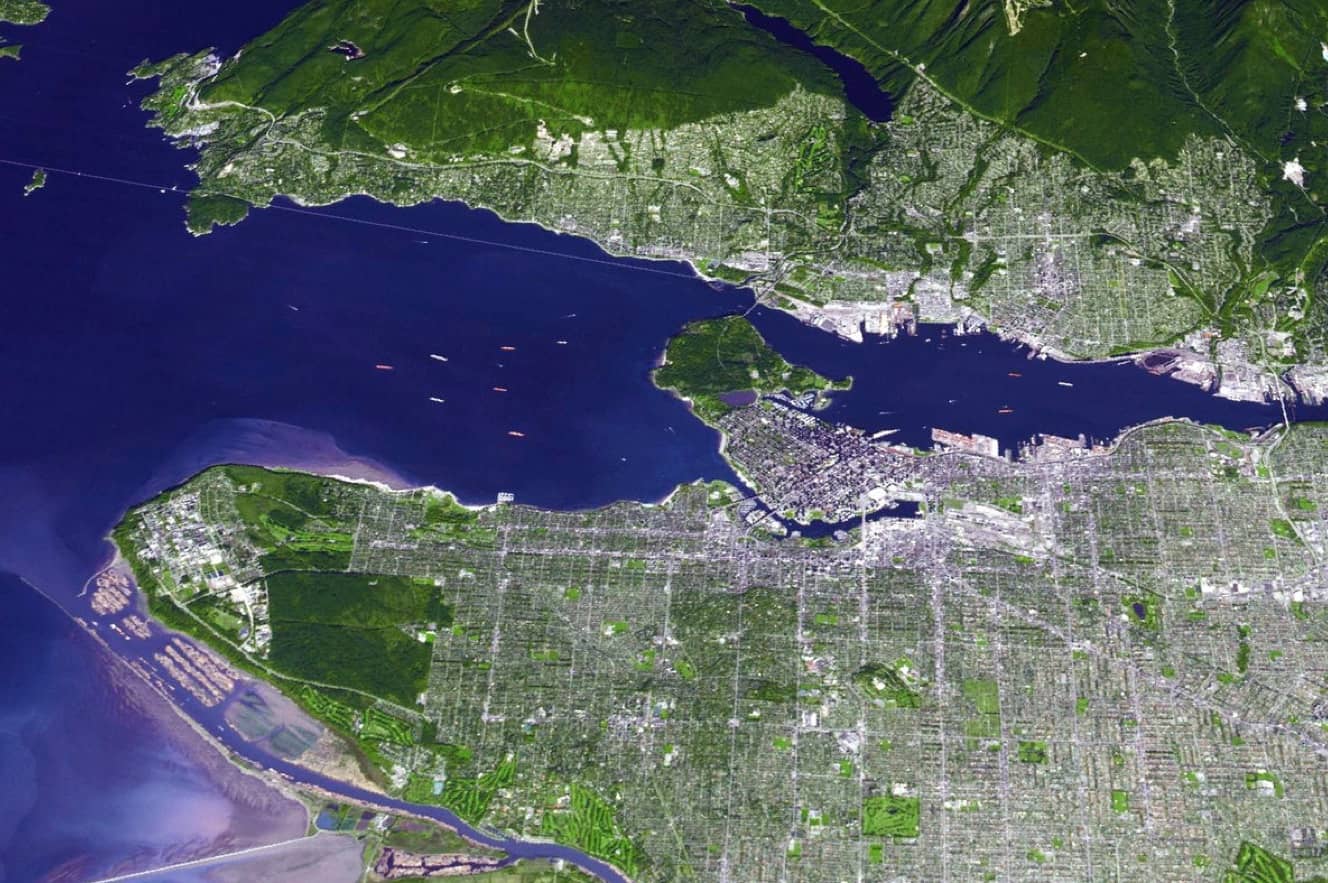
A case study applies the model to the Sunset region of Vancouver, Canada. The case study explored three urban-form policy experiments: dispersed, commercial corridor, and transportation-oriented development (TOD). The analysis illustrates the combined results of a technology policy regulating a shift towards electrification and a spatial urban form densification policy. The authors identify specific growth-management strategies that can be more effective for reducing emissions than when integrated with other urban form strategies.
Policies focused on energy
and emissions standards for new buildings will be relatively more effective in
areas with a growth-management strategy that necessitates the redevelopment of
many existing buildings. This demonstrates a useful approach for understanding
exactly which policy instruments, such as densification, higher building energy
standards, and fuel switching, will bring the most emissions reductions.
Funding
The research was funded by Pacific Institute for Climate Solutions (PICS). Additional funding from Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) Canada and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) supported tool development and related research.
Reference
Lu, Y., Scott, A., Kim, J. C., Curi, C. B., McCarty, J., Pardy, A., Rysanek, A., Girling, C & Kellett, R. (2021). Integration of an energy-economy model with an urban energy model. Buildings and Cities, 2(1), 114-133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/bc.71Latest Peer-Reviewed Journal Content
Acceptability of sufficiency consumption policies by Finnish households
E Nuorivaara & S Ahvenharju
Key factors for revitalising heritage buildings through adaptive reuse
É Savoie, J P Sapinski & A-M Laroche
Cooler streets for a cycleable city: assessing policy alignment
C Tang & J Bush
Understanding the embodied carbon credentials of modern methods of construction
R O'Hegarty, A McCarthy, J O'Hagan, T Thanapornpakornsin, S Raffoul & O Kinnane
The changing typology of urban apartment buildings in Aurinkolahti
S Meriläinen & A Tervo
Embodied climate impacts in urban development: a neighbourhood case study
S Sjökvist, N Francart, M Balouktsi & H Birgisdottir
Environmental effects of urban wind energy harvesting: a review
I Tsionas, M laguno-Munitxa & A Stephan
Office environment and employee differences by company health management certification
S Arata, M Sugiuchi, T Ikaga, Y Shiraishi, T Hayashi, S Ando & S Kawakubo
Spatiotemporal evaluation of embodied carbon in urban residential development
I Talvitie, A Amiri & S Junnila
Energy sufficiency in buildings and cities: current research, future directions [editorial]
M Sahakian, T Fawcett & S Darby
Sufficiency, consumption patterns and limits: a survey of French households
J Bouillet & C Grandclément
Health inequalities and indoor environments: research challenges and priorities [editorial]
M Ucci & A Mavrogianni
Operationalising energy sufficiency for low-carbon built environments in urbanising India
A B Lall & G Sethi
Promoting practices of sufficiency: reprogramming resource-intensive material arrangements
T H Christensen, L K Aagaard, A K Juvik, C Samson & K Gram-Hanssen
Culture change in the UK construction industry: an anthropological perspective
I Tellam
Are people willing to share living space? Household preferences in Finland
E Ruokamo, E Kylkilahti, M Lettenmeier & A Toppinen
Towards urban LCA: examining densification alternatives for a residential neighbourhood
M Moisio, E Salmio, T Kaasalainen, S Huuhka, A Räsänen, J Lahdensivu, M Leppänen & P Kuula
A population-level framework to estimate unequal exposure to indoor heat and air pollution
R Cole, C H Simpson, L Ferguson, P Symonds, J Taylor, C Heaviside, P Murage, H L Macintyre, S Hajat, A Mavrogianni & M Davies
Finnish glazed balconies: residents' experience, wellbeing and use
L Jegard, R Castaño-Rosa, S Kilpeläinen & S Pelsmakers
Modelling Nigerian residential dwellings: bottom-up approach and scenario analysis
C C Nwagwu, S Akin & E G Hertwich
Mapping municipal land policies: applications of flexible zoning for densification
V Götze, J-D Gerber & M Jehling
Energy sufficiency and recognition justice: a study of household consumption
A Guilbert
Linking housing, socio-demographic, environmental and mental health data at scale
P Symonds, C H Simpson, G Petrou, L Ferguson, A Mavrogianni & M Davies
Measuring health inequities due to housing characteristics
K Govertsen & M Kane
Provide or prevent? Exploring sufficiency imaginaries within Danish systems of provision
L K Aagaard & T H Christensen
Imagining sufficiency through collective changes as satisfiers
O Moynat & M Sahakian
US urban land-use reform: a strategy for energy sufficiency
Z M Subin, J Lombardi, R Muralidharan, J Korn, J Malik, T Pullen, M Wei & T Hong
Mapping supply chains for energy retrofit
F Wade & Y Han
Operationalising building-related energy sufficiency measures in SMEs
I Fouiteh, J D Cabrera Santelices, A Susini & M K Patel
Promoting neighbourhood sharing: infrastructures of convenience and community
A Huber, H Heinrichs & M Jaeger-Erben
New insights into thermal comfort sufficiency in dwellings
G van Moeseke, D de Grave, A Anciaux, J Sobczak & G Wallenborn
'Rightsize': a housing design game for spatial and energy sufficiency
P Graham, P Nourian, E Warwick & M Gath-Morad
Implementing housing policies for a sufficient lifestyle
M Bagheri, L Roth, L Siebke, C Rohde & H-J Linke
The jobs of climate adaptation
T Denham, L Rickards & O Ajulo
Structural barriers to sufficiency: the contribution of research on elites
M Koch, K Emilsson, J Lee & H Johansson
Disrupting the imaginaries of urban action to deliver just adaptation [editorial]
V Castán-Broto, M Olazabal & G Ziervogel
Nature for resilience reconfigured: global- to-local translation of frames in Africa
K Rochell, H Bulkeley & H Runhaar
How hegemonic discourses of sustainability influence urban climate action
V Castán Broto, L Westman & P Huang
Fabric first: is it still the right approach?
N Eyre, T Fawcett, M Topouzi, G Killip, T Oreszczyn, K Jenkinson & J Rosenow
Social value of the built environment [editorial]
F Samuel & K Watson
Understanding demolition [editorial]
S Huuhka
Data politics in the built environment [editorial]
A Karvonen & T Hargreaves


Latest Commentaries
Decolonising Cities: The Role of Street Naming
During colonialisation, street names were drawn from historical and societal contexts of the colonisers. Street nomenclature deployed by colonial administrators has a role in legitimising historical narratives and decentring local languages, cultures and heritage. Buyana Kareem examines street renaming as an important element of decolonisation.
Integrating Nature into Cities
Increasing vegetation and green and blue spaces in cities can support both climate change mitigation and adaptation goals, while also enhancing biodiversity and ecological health. Maibritt Pedersen Zari (Auckland University of Technology) explains why nature-based solutions (NbS) must be a vital part of urban planning and design.